Methazolamide
General Information
Methazolamide Impurities and Methazolamide
For evaluating the purity and safety of Methazolamide, an active pharmaceutical ingredient, Daicel Pharma offers a customized synthesis of Methazolamide impurity standards. These impurity standards include crucial compounds such as Methazolamide impurity-C and N-(5-(benzylthio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-N-methylacetamide. Additionally, Daicel Pharma provides worldwide delivery options for Methazolamide impurity standards.
A sulfonamide derivative, Methazolamide [CAS: 554-57-4], acts as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, offering potential antineoplastic effects. In addition to its antineoplastic activity, Methazolamide is a diuretic and treats glaucoma.
Methazolamide: Use and Commercial Availability
Neptazane is the brand name of a sulfonamide derivative, Methazolamide. It acts as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) in wide-angle and secondary glaucoma, and is used before surgical intervention for severe wide-angle glaucoma.
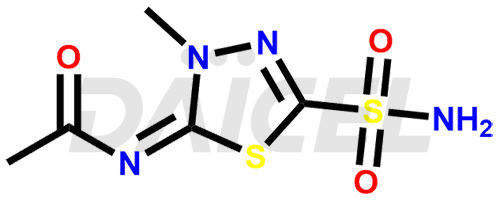
Methazolamide Structure and Mechanism of Action 
The chemical name of Methazolamide is N-[5-(Aminosulfonyl)-3-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-ylidene]acetamide. Its chemical formula is C5H8N4O3S2, and its molecular weight is approximately 236.3 g/mol.
Methazolamide inhibits carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye. It reduces aqueous humor secretion and slows the formation of bicarbonate ions.
Methazolamide Impurities and Synthesis
Methazolamide1, a sulfonamide derivative, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, may contain impurities that can impact its quality and effectiveness. They can be related substances, residual solvents, or degradation products. It maintains strict quality control during the manufacturing process and storage of Methazolamide to minimize impurity levels and ensure its safety and efficacy.
Daicel Pharma strictly adheres to cGMP standards and operates an analytical facility for preparing Methazolamide impurity standards, which include Methazolamide impurity-C and N-(5-(benzylthio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-N-methylacetamide. Our Methazolamide impurity standards have a detailed Certificate of Analysis (CoA) that provides a comprehensive characterization report. This report includes data obtained through techniques, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity analysis2. Upon request, we give additional data like 13C-DEPT. Moreover, we can synthesize unknown Methazolamide impurity standards and degradation products. Each delivery has a comprehensive characterization report.
References
FAQ's
References
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there specific guidelines for controlling organic Methazolamide impurities?
Specific guidelines exist for controlling organic impurities in Methazolamide. The International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) has published guidelines such as ICH Q3A(R2) and Q3B(R2), which provide recommendations for the identification, qualification, and control of organic impurities in pharmaceuticals.
Can Methazolamide impurities impact its bioavailability?
Yes, impurities in Methazolamide can potentially affect its bioavailability. They may interact with the drug molecule, altering its solubility, absorption, or metabolism. Their control helps maintain the drug's bioavailability and ensure consistent therapeutic outcomes.
Which solvent helps in analyzing Methazolamide impurities?
Methanol is the solvent used when analyzing most impurities in Methazolamide.
What is the recommended storage temperature for Methazolamide impurities?
Methazolamide impurities should be stored, at a controlled room temperature, usually between 2-8 °C.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.