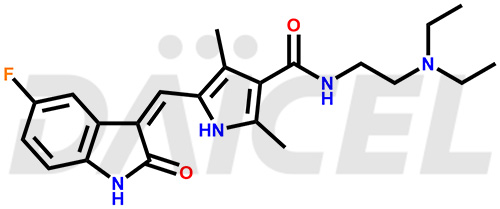
Sunitinib
General Information
Sunitinib Impurities and Sunitinib
Daicel Pharma is a reliable source for synthesizing high-quality Sunitinib impurities, (Z)-N-(2-(ethyl(nitroso)amino)ethyl)-5-((5-fluoro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)methyl)-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide, N-(2-aminoethyl)-N-ethylnitrous amide, Sunitinib N-Oxide, etc. These impurities help in analyzing the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient Sunitinib. Additionally, Daicel Pharma specializes in the custom synthesis of Sunitinib impurities, catering to specific client requirements. These high-quality impurities can be shipped globally, offering convenience and flexibility to customers worldwide.
Sunitinib [CAS: 557795-19-4] is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor for treating renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST).
Sunitinib: Use and Commercial Availability
Sunitinib is a medication to treat a rare stomach cancer, bowel, or esophagus called a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). It also treats advanced renal cell carcinoma and a type of pancreatic cancer called pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET).
Sunitinib is available under Sutent, which contains the active ingredient, Sunitinib.
Sunitinib Structure and Mechanism of Action 
The chemical name of Sunitinib is N-[2-(Diethylamino)ethyl]-5-[(Z)-(5-fluoro-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide. Its chemical formula is C22H27FN4O2, and its molecular weight is approximately 398.47 g/mol.
Sunitinib inhibits multiple RTKs that cause tumor growth and cancer. It also has inhibitory action against platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFRa and PDGFRb), vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3), and other kinases.
Sunitinib Impurities and Synthesis
During Sunitinib’s manufacturing1, impurities form that compromise its effectiveness. They can arise from various sources, including the raw materials, intermediates, and chemicals utilized to synthesize Sunitinib. Closely managing and monitoring these impurities is paramount to ensure the drug’s optimal efficacy and safety.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for Sunitinib impurity standards, encompassing impurities such as (Z)-N-(2-(ethyl(nitroso)amino)ethyl)-5-((5-fluoro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)methyl)-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide, N-(2-aminoethyl)-N-ethylnitrous amide, Sunitinib N-Oxide, etc. The CoA provides detailed characterization data, including 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. Additionally, we give a detailed 13C-DEPT upon delivery. With advanced technology and expertise, Daicel can synthesize any unknown Sunitinib impurity or degradation product. We also supply labeled compounds.
References
FAQ's
References
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the presence of impurities a concern in Sunitinib?
Impurities in Sunitinib can affect its quality, safety, and efficacy. Depending on the type and level of impurities, they can impact the drug's pharmacological activity and stability and pose potential risks to patient health.
How are impurities in Sunitinib detected and quantified?
Impurities in Sunitinib are detected and quantified using reversed-phase (RP) ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. This method will allow for accurate identification and quantification of impurities.
What steps can control impurity levels in Sunitinib during manufacturing?
To maintain control over impurity levels in Sunitinib, several strategies, like using high-quality starting materials, optimizing synthesis, comprehensive quality-control tests, and continuously monitoring impurity levels, must be implemented at different stages of the manufacturing process.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Sunitinib Impurities?
Sunitinib Impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8°C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.